The Use of Poseable Mannequins During Bowling Motor Skill Training
Originally published in Bowling This Month
All athletes go through several stages during the process of motor skills training.
During the first stage, the athlete must be given all the information needed to form an image of the movement being practiced in his or her mind.
The next stage is when the athlete starts to master the new movement. This stage is characterized by the conscious control of all actions, slow movements, a significant amount of errors, and being easily distracted by external or internal stimuli.
The final stage of skill mastery is evident when the athlete starts performing movements automatically, without conscious control, using an optimal rate of movement, with an error rate that is trending to zero, and has a stable resistance to external or internal distractions.
Forming the image of the skill in the mind
The role of the first stage of mastering a skill is often underestimated. It is critical that the information be delivered in a way that is accessible and understandable to the student so that they can form the correct image of movement within their mind. In my observations, sometimes 15 minutes effectively spent at this stage can save dozens of hours of training in the later stages of mastering a skill.
This important first stage will be discussed in this article, and I will include my experience with optimizing this process. Future articles will cover the next two stages.
Methods of image formation
As a coach, one must use all possible channels of education to help the athlete create the correct execution of the skill within their minds. The visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learning modalities should be used effectively as needed for each student. In general, the effectiveness of training will increase significantly when a combination of these modalities is utilized.
In fact, the uptake rate and quality of understanding increase dramatically when combining all three perception channels. Research has shown that when using just auditory or visual channels separately, only 10% of new information is absorbed. The combination of audio and video helps to increase the uptake level to 50%. Adding the kinesthetic channel to the other two provides an optimal rate of 90% of new information being understood. Thus, the integrated approach of using all three learning modalities is the most efficient. Of course, the coach needs to recognize and take advantage of the athlete’s dominant channel of perception.
During the initial stage of skill training, it is necessary to create a complete field of information for a given skill set.
During the later stages of skill encoding, the most efficient implementation is to work with the channel of perception which “delivers” information in the form closest to the type and kind of thinking directly involved in the learning process and the implementation of a given skill. For example, when mastering a skill that predominantly uses spatial and visual thinking, it is usually most efficient to use the visual channel as the dominant one and the others as complementary. Or, if the proprioceptive senses are mostly involved, it is recommended to use the kinesthetic channel of perception as the dominant one and the other channels as complementary.
The critical role of spatial and visual thinking in bowling skill-building
Spatial thinking is an activity that helps the athlete create mental images which they can adapt to solve practical and theoretical problems. Following this definition, we understand that it is this kind of thinking that is dominant when we are teaching and training different skills in bowling. A well-developed sense of spatial thinking will greatly enhance the bowler’s ability to learn and understand many physical and analytical skills related to bowling.
In the bowling alley, where in addition to a good technical throw, the player is required to understand motion phase analysis of the ball along it’s path (skid, hook, and roll), changes in the oil pattern, types of pin action, and much more. In virtually all stages of the training process, spatial and visual thinking modalities are absolutely essential tools for a player’s success. Equally important is the development and the effective use of these kinds of learning modalities for the coach’s success in training their athletes.
Spatial and visual thinking in forming motor imagery
Spatial and visual thinking allows a player to simultaneously work on understanding technical elements of the physical game as well as forming motor imagery in the player’s mind (i.e. it can be used as the first stage of motor skill formation). Some elements of this technique are similar to the motor imagery practice, but it is simpler to use and does not require special training.
We must simplify the process of mentally visualizing a technique to the point that the player can easily press “play” in their mind in order to see the technique played out. The creation of a mental image of a practiced movement is a prerequisite for its further improvement. The rate of a player’s improvement depends largely on the degree of detail and accuracy given to this mental imagery. Plus, fine motor skills will be used to develop such thinking skills as reaction time, attention, coordination, imagination, observation, and visual and motor memory.
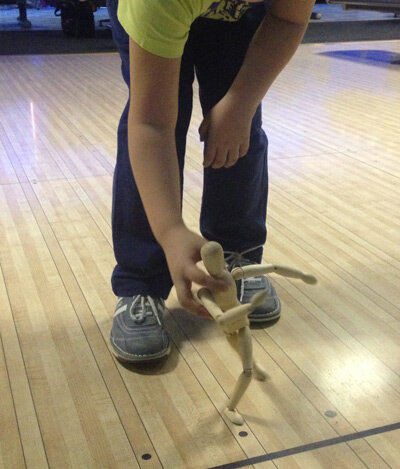
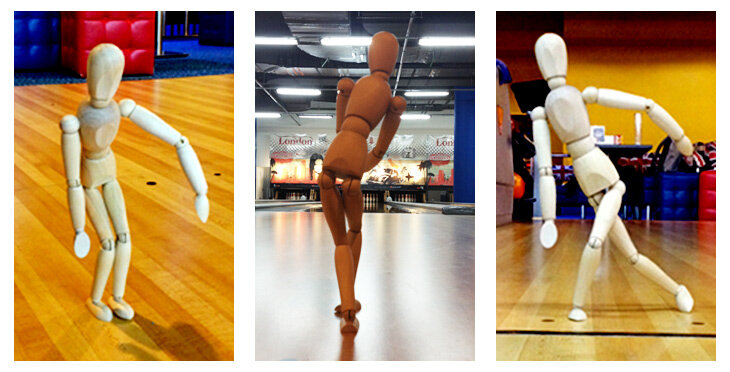
For using this training method, three things are needed: a video of a student’s shot, a video of an equivalent master’s shot (i.e. a bowler with similar physical and mental traits to the student), and a 12 inch tall mannequin, such as one used by art students and sold in stores like IKEA, Hobby Lobby, Michael’s, etc. Examples of the type of mannequins which are effective for this type of training are shown below.
A small artist’s mannequin can be used to demonstrate physical poses during training.
The coach and the student view the video of the student’s shot and discuss the technical elements which are to be worked on.
The coach and the student view the video of the equivalent master shot and, once again, discuss the technical elements.
Using the mannequin, create images of the necessary technical elements.
Set the mannequin in the approach area of a lane or on the layout of a bowling lane for a more complete and correct understanding of the player’s position in the space.
At the end of the process, ask the student to mentally reproduce all the movements in sequence.
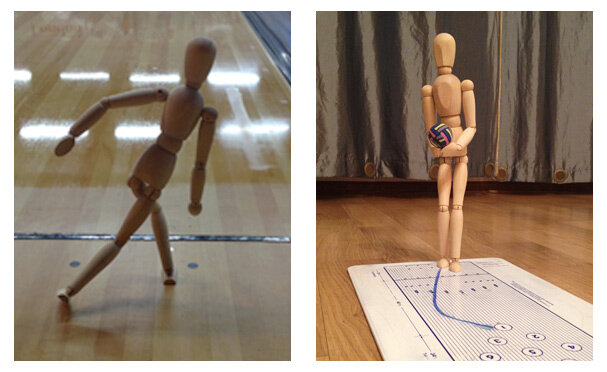
The mannequin can be used both on-lane and on top of a bowling lane overlay, such as the clipboard overlay shown.
After a while, your students will be able to easily adjust the image of the necessary technical elements in full, and “play” it at will in their imagination. This method is especially effective for young players.
Use of the mannequin during training sessions involving young bowlers is especially effective.
Often, this method of training is not only useful, but it is also is a lot of fun. Give it a try in your own coaching sessions and see for yourself!
Jedi Bowling: Line-of-sight construction skill and the methods of its training
Originally published in Bowling This Month
“Skill” is the ability to carry out an action automatically without active conscious control. An indicator of skill competence is performance of an action without the need to consciously think about how the action will be performed. When a person has skill competence for a given task, it is no longer necessary to think about the execution of the skill via its separate partial sub-operations.
Successful bowling, of course, requires competence in countless complex skills. One of the many jobs of the bowling coach is to develop and use the most effective methods of skill training on our students so that their learning processes can be accelerated as much as possible.
In this article, I want to analyze the process of learning and the implementation of one specific bowling game skill. Namely, we will examine the line-of-sight construction skill of the bowler. Line-of-sight construction is a skill that allows the bowler to envision the launch trajectory of the bowling ball on the lane. We’ll start with some background and with a description of why this skill (as well as other similar skills) can be so challenging to teach. Finally, we will give an example of a new method of line-of-sight training that I’ve been using successfully with my own students to accelerate their development.
Background and motivations
Throughout my career as a bowling coach, I’ve had the opportunity to work with a wide variety of bowlers. This includes players at the novice level all the way up to the national team level.
Additionally, I have a significant amount of experience coaching deaf bowlers. One of my students is a medalist in the Deaflympics and numerous of my other deaf students are European Bowling Championship winners. Recently, one of my female deaf students won a Gold medal at the 3rd World Deaf Bowling Championships in Bologna, Italy in August 2015.
Working with bowlers who have different types of thinking skills has motivated me to seek out improved teaching methodologies for our sport. The task of building an efficient training process for deaf bowlers, for example, has been very non-trivial. This led me to deeply analyze the process of bowling skill learning from the perspectives of cognitive and educational psychology.
This process uncovered psychological regularities of the bowling training process. Developing an understanding of these regularities has resulted in me adjusting my training methods for improved efficiency. This has led to significant accelerations in skill mastery for players of all types.
Line-of-sight construction is one particular bowling skill that can be challenging to teach to both deaf bowlers and many non-deaf bowlers alike. Let’s start by taking a close look at this skill and the current methods of its teaching.
Line-of-sight construction: one of bowling’s fundamental skills
Bowling is a complex skill that involves perceptual, intellectual, and motor abilities of the player. In these ways, it is quite similar to other complex skills, such as learning to control an aircraft, for example. The ability to:
construct motion paths,
control physical efforts,
feel position in space,
make quick decisions about the current situation,
perform standard operations, and
know and apply correctly a set of rules
All are features of both bowling and controlling an aircraft. Many complex activities in a wide variety of disciplines share these same characteristics.
In bowling, line-of-sight construction is an important skill related to targeting that must be developed by bowlers of all levels. This skill is chosen as an illustration due to its importance in the overall structure of the bowling training process.
The ability to envision the line-of-sight on the lane, to keep it in the mind during the bowling approach, and to subsequently analyze the delivery with respect to the line-of-sight allows the bowler to effectively solve a wide range of tasks, such as:
positioning himself in space and correctly performing the physical game elements relative to the given line;
making a correct analysis of the accuracy of a delivery and of the dynamic characteristics of the ball motion on the lane;
making decisions on the necessary changes in ball trajectory and then rapidly implement them;
and much more!
Thus, the described skill of line-of-sight construction is one of the basic skills of our sport. The degree of its mastery defines the speed of a player successfully training the rest of the skills of bowling. It can be an indicator of his success as a whole on the lanes. In fact, the development of this skill is one of the first tasks facing a coach while training a new player in our sport.
Bowler skill level vs. line-of-sight construction skill mastery level
While preparing this article, I have performed testing of bowling players on their mastery of line-of-sight construction skill and found correlations between the players’ success on the lanes and the extent to which they’ve mastered this skill. Here are some brief details of the results of this study:
Entry-level bowlers: Often cannot imagine and describe in words the ball trajectory on the lane; are not visually concentrating on the point of sight during delivery preparation and execution; often use hitting the pins as an accuracy criterion; have no clear image of the line-of-sight.
Mid-level bowlers: Can describe in words the ball trajectory on the lane; are concentrated on the point of sight (sometimes excessively) during delivery preparation and execution; use assessment of hitting the point of sight as an accuracy criterion; the line-of-sight image is in the forming stage.
Advanced bowlers: Can describe the ball trajectory with precise detail in any area of the lane; are concentrated on the line-of-sight duringdelivery preparation and execution, with the ability to change the visual concentration to various points of sight along the line; use assessment of hitting the line-of-sight as an accuracy criterion detailed in various zones of the lane; the image of the line of sight is clearly formed in the visual imagination of the player and is used with no effort during delivery preparation and execution.
As the results of this test show, there is significant correlation between overall bowler skill level and line-of-sight construction skill level.
Current methods of line-of-sight skill training
All existing targeting systems in bowling are built on the principle of line-of-sight construction on the lane. Differences in targeting systems are only in using different markers as the coordinate system for the line of throw construction (targets, pins, breakpoints, exit points, laydown points, starting position of the player, and so on). The final aim of all systems is a line construction on the lane surface and in the approach area.
Operating with initial data in accordance with the theory of the throw line construction voiced by the coach, the player must use abstract logical, spatial, and visual imagination to construct the throw line on the lane and in the approach area. The player must then hold his concentration to perform a delivery, controlling his own movements and the subsequent movement of the ball relative to this imagined line.
If it is necessary to change the ball trajectory, the player (using information provided by the coach) must recalculate the coordinates of the required markers and construct a new line. This is not an easy task. The main problem is in the constant interaction of abstract logical and visual representation types of thinking.
Even when a player is given initial information in the form of visual images and tips from his coach, the transfer of these images to the real lane is always performed in the mind of the player. In such a case, it is impossible to avoid the process of personal interpretation.
Solving this problem, we are increasingly becoming dependent on the features and level of a player’s abstract logical thinking and the abilities of his mental apparatus regarding the interpretation and transferring of the abstract logical concepts into symbols and images used by visual and representation thinking.
If the player is talented in this respect, we get the correct image in his mind and we get it very rapidly. For other players, perhaps even those who are more gifted in physical and coordination abilities, this task may be very difficult. It may either take a long time to perform, or it may not even be solved at all.
“So what?” you might object to me. “Successful bowling is about survival of the fittest; the most talented players will succeed and thrive!”
In my opinion, the difficulty of solving this problem for the player is not so much due to the level of the player’s ability. Instead, the difficulty is caused by the method of supplying the initial information and the proposed algorithms of solution. Too large of a role of abstract and logical thinking in the described processes can be destructive.
We as bowling coaches are a lot like a teacher who tries to solve the problem of constructing and fixing in a pupil’s visual memory the image of a 90 degree angle. Doing this using only a verbal description is quite difficult. Even if the teacher is permitted to draw two randomly-arranged straight line segments and then explain in words how to form a 90 degree angle from them, it is still an incredibly difficult task.
Alternatively, just draw two perpendicular lines, show the angle, and then add any verbal description for better understanding. The result is instant and the student immediately understands the concept of a 90 degree angle!
A proposed new technique for bowling line-of-sight construction training
I will now introduce a new method of line-of-sight construction training that I have used with great success with many of my students. The method involves using a device to create and consolidate in the spatial and visual imagination and in the memory of the player a bright image of the line-of-sight in the real playing environment during delivery preparation and execution.
While training using this device, there is no need to describe the line image using objects of abstract logical thinking, and, as a consequence, there is no need for any interpretation by the player.
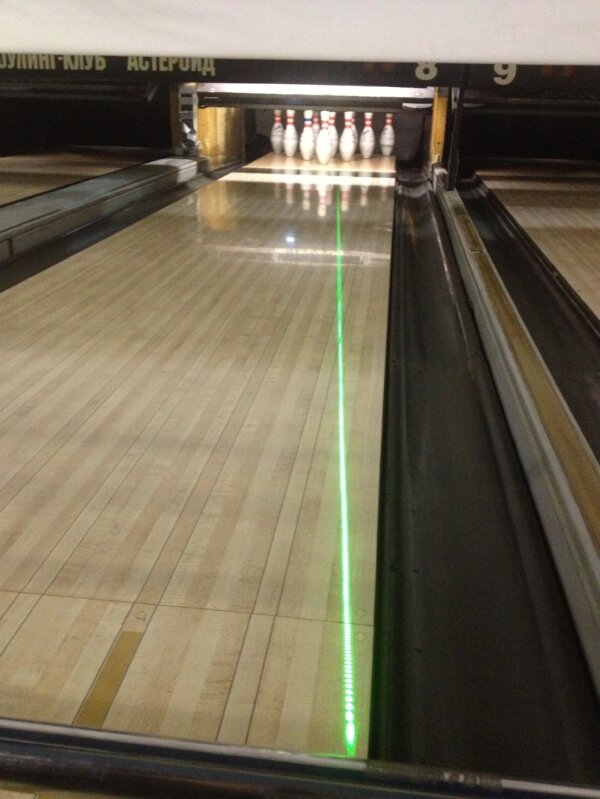
This patent-pending device utilizes a luminous bar (3 to 5 meters high) installed above the lane in a vertical position. Depending on the particular training task, it can be installed in the targeting area, at the exit point, at the breakpoint, or as close as possible to pins. Reflection of this bar creates a bright and clearly visible image of the line-of-sight on the lane. This bright reflected line on the lane is used to train and consolidate the required skill of constructing the line-of-sight by the bowler.
Lighted bar, installed in the breakpoint zone
The property of the reflected line to change its position while the player moves left and right, as well as the possibility to change the initial position of the device, allows the bowler to almost intuitively understand the process of adjusting the line position on the lane.
Since this training technique so directly demonstrates the concept of line-of-sight and its fundamental properties, it is even effective on players who haven’t yet developed advanced abstract logical thinking abilities, such as children.
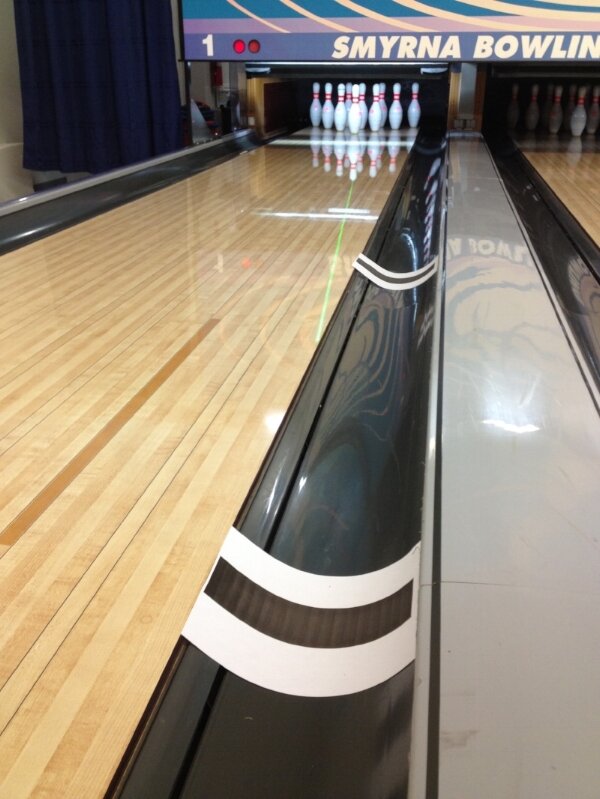
Here, the lighted bar is installed at the arrow zone for the purposes of 3-6-9 training.
Besides the basic training function of teaching a bowler how to construct the line-of-sight, use of this device has generated four important additional benefits:
Hitting or nearly hitting the line visible by the player is only possible with correct technical throw execution.
The possibility to assess visually the dynamics of the line-of-sight movement along the lane by the player during the delivery creates conditions for more effective correction and monitoring of the spatial and technical elements of the approach. This creates a very effective instant feedback system for the bowler.
It becomes possible to see a diagram of oil application on the lane and its variations, because due to different oil amounts in different areas of the lane, the reflection coefficient of the light source varies. As a result, the thickness of the oil in different zones and the dynamics of its changes during play become visible to the bowler.
The reflected light line creates the possibility of performing a visual assessment of lane topography. The curvature of the reflected line shows the deviation of the lane plane from the horizontal plane.
Here are some additional videos of the lighted bar in use during training, both as viewed from the coach’s position behind the approach and as viewed through the eyes of the bowler.
Results
The practical use of this technique has shown that it has high efficiency. The image of the line-of-sight is quickly fixed in the visual memory of the player. After just a few training deliveries, it is not difficult for most players to use this image, even in the absence of the training device.
Mastering the line-of-sight construction skill has become much faster. Testing has shown that the time duration of mastering this important skill is reduced significantly (sometimes by an order of magnitude) through the use of this device and this training method. Additionally, the skill is successfully mastered by players regardless of the development of their abstract logical and visual representation thinking.
Often, after a month of training using this technique, entry-level players show a skill mastery level comparable to that of advanced players. This allows them to progress more quickly in their future training.
Practical considerations and next steps
Some of you might be wondering about the practicality of the above-described training method. It is true that it does require some special equipment. Also, like all things that happen beyond the foul line, use of such equipment requires agreement and cooperation with the bowling center owner.
As of now, there is no commercially-available “off-the-shelf” luminous bar line-of-sight training system. However, it is a fairly simple design that can be constructed from components that are readily available. It can be installed on the lane in about five minutes and removed in three minutes. Also, I have built and used a version of this system that is fully portable. Development of a ready-made system that can be purchased by coaches is a possibility for the future.
Conclusions
I hope you have enjoyed this introduction to some of the challenges in bowling skill training and that I have opened your eyes to the opportunities that exist in developing more efficient training methods for our sport. As previously mentioned, I have studied the theory of effective learning and skill development for bowling extensively. I have many other ideas in different areas of bowling skill development, such as timing training, swing direction training, ball reaction understanding, and more. I hope to share them with you in upcoming articles.
Finally, I welcome your questions, comments, and suggestions, as they will be very beneficial in helping me decide on content for future contributions.
Entry Angle Assessment
Originally published in Bowling This Month - February 2016
In modern bowling, a player’s success depends on the implementation of numerous components: throw execution, ability to measure the characteristics of ball motion, mental and psychological preparedness, and much more. In this article, I want to share my experience in teaching the skill of determining the bowling ball’s entry angle. Mastering this skill allows the player to quantitatively assess one of the major characteristics of ball motion and enables deliberate correction of numerous game components.
In this skill, as well as the line-of-sight construction skill (described in my previous article), visual and spatial thinking are critical. We have to pay the most attention to these types of thinking when learning and using both line-of-sight construction and entry angle assessment skills. When testing players at different levels, most players, including advanced ones, could not determine the value of their ball’s entry angle. In the majority of cases, they could provide only a simple and ambiguous description, such as small, large, insufficient, bad, too much, etc.
This is not surprising, since very few players have had the opportunity to assess this parameter using the currently-available technical feedback systems that provide entry angle data (such as CATS and others). In practice, the skill of entry angle determination is almost always developed over many years of training and long tournament practice. On the other hand, applying the training methods described below, it is possible to obtain improved results in significantly less time, wherein players, using their spatial and visual thinking and memory, are able to determine the entry angle quantitatively using a range from 3 to 6 degrees.
When we evaluate trajectory accuracy characteristics, the lane markings (counting of boards and/or targets) allow us to see and quantitatively assess the ball’s lateral position in different parts of the lane (target area, breakpoint area, position of the ball at pin contact, etc.). This allows us to literally name the number of a board on which the ball is positioned at any given point along its trajectory. For example, when we need to draw the line-of-sight, we can use readily visible marks, such as targets, pins, dots, etc. In contrast, it is difficult to determine the entry angle on the lane due to the absence of readily visible and memorable orienting points.
Laser line projection
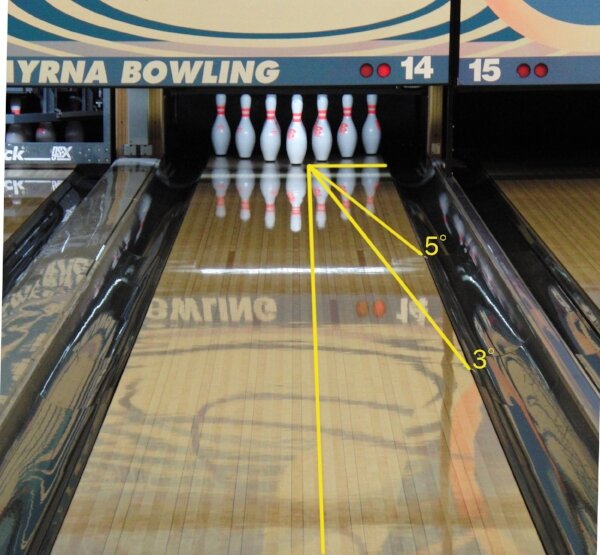
To overcome this lack of orienting points, the student first and foremost needs to be shown the image of the entry angle line on the lane and how the entry angle is determined. For this purpose, a special line laser can be used to “draw” the entry angle line on the lane.
An entry angle line of 5 degrees “drawn” onto the lane with a green line laser.
During the initial training phase, it is important that the student does not focus on the entry angle value. It is most important for the student to see the image of the entry angle line on the lane and memorize that image. A good starting point is to mark the angle at 4 degrees and ask the player how the entry angle of his throw differed from the visible one on the lane.
A powerful memorization technique is for the coach to quickly move the visible entry angle line to reflect the characteristics of the specific player’s throw in order for the ball to pass along the visible line as often as possible. Thus, the player will quickly learn to determine the presence or absence of ball roll as well as the length of the ball roll. This is a very important and useful intermediate skill!
Editor’s note
Laser setup example
The laser line in the above image was generated using a standard off-the-shelf 350 mW green laser pointer in conjunction with an off-the-shelf line lens kit, with the laser mounted on a tripod, as shown.
Please be advised that lasers can be dangerous. A 350 mW laser is a Class 3B laser device which can cause harm if used improperly. Among other risks, never look directly into the beam of a laser and never point a laser beam at a person. Never use a laser unless you are properly trained and understand all the possible risks. Also, please keep in mind that the sale and use of lasers can sometimes be subject to government regulations.
It doesn’t take long for the student to memorize the entry angle image when using a bright and memorable laser line. Once the player fully understands these concepts, the next step is to learn how this line ties into a coordinate system which provides the framework to make the necessary quantitative assessment to determine the angle value correctly in the absence of the laser line. There are two very helpful methods for this purpose.
Intervals
The first one is the method of intervals. With this method, the player is taught to quickly analyze and determine various lengths on the lane correctly. In principle, this skill is very important for understating ball reaction.
The goal is for the student to memorize the most important intervals on a lane, including 30 feet, 35 feet, 40 feet, 45 feet, and 50 feet. We approach this task by placing memorable marks, such as paper taped in the gutter, at the desired length or lengths.
An example of using paper markers in the gutter to show the location of specific distances.
An example of using paper markers in the gutter to show the location of specific distance. Of course, this is assuming that the player understands basic lane geometry (such as the width of lane, the distance to the targets and pins, etc.), since memorizing the desired unmarked points requires that the student use all available visual cues. For instance, the 1st pin (at 60 feet) has a reflection that can either correspond to or be very close to one of the desired intervals (50 feet for a taller person, down to 45 feet for a shorter person). Determine what interval the bowler sees and use it.
It is important to understand that the intervals are determined by the individual’s unique characteristics, since they are connected with the player’s height and the height of his eyes in the initial and finish positions. To begin with, focus on memorizing the required intervals from the player’s finish position, as it is critical to choose a consistent and repeatable position from which to memorize visual cues. Moreover, this is yet another argument for the benefit of a stable and proper finish position. Obtaining visual information after releasing the ball from the foul line is facilitated by correct and consistent technical execution.
For entry angle determination, memorizing just the two lengths of 30 feet (half the distance from the foul line to the first pin – 1/2 of the lane) and 45 feet (half the distance from the 30 feet mark to the first pin – 3/4 of the lane) is enough. It is easiest to start by memorizing the 30 feet mark and then later adding the 45 feet mark. Once the student has memorized these intervals, the next training session can focus on learning how these lengths relate to the two entry angles of 3 degrees and 5 degrees.
Ideally, using two laser lines, the coach should indicate the 3 degree line extending from 31 feet to the pocket and the 5 degree line from 42.5 feet to the pocket. Remembering the memorized visual cues for 30 and 45 feet, the student can simply add 1 foot for the 3 degree line and subtract 2.5 feet for the 5 degree line in order to commit these angles to memory.
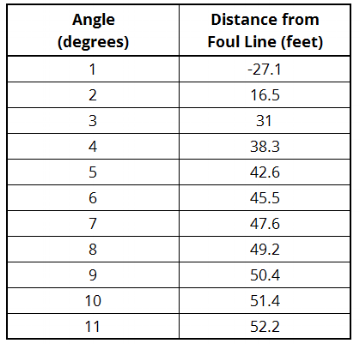
In order to achieve different entry angles, balls and throw execution parameters (speed of throw, axis tilt, ball trajectory, etc.) can be changed. The table below shows the entry angle which corresponds to the given length of the lane edge from the foul line.
Angle vs. distance for a line drawn from the gutter edge to the pocket.
At this point, the student has learned a significant and complex skill set: a practical understanding of the detailed range of his ball arsenal and the effect of changing throw characteristics on the ball trajectory.
The use of a device for marking the aiming line, described in my previous article, in combination with marking the entry angle line(s), is an efficient technique for teaching the player to consolidate these skills.
Retinal angle assessment
For further consolidation of this newly acquired skill, there is another approach to memorizing the entry angles that a player sees. Have you ever asked a beginning student or spectator about the entry angle value they perceive? The answer is consistently 45 degrees. This is accurate if the angle is assessed as obtained by the retina at the foul line. It matches the angle measured on video or photos.
A bowler’s perception of entry angle is typically very large (shown from a height of 4.5 feet at the foul line).
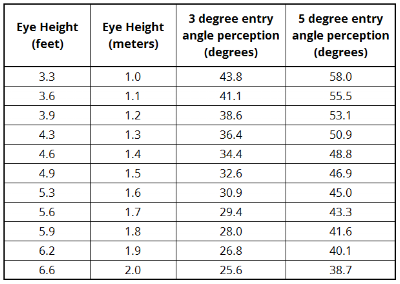
Retinal angle assessment can be used to obtain the true angle. In order to do this, the coach must determine the characteristics of the player that will influence their perception of the entry angle. The table below shows the height of the player’s eyes at the finish position which corresponds to their perception of 3 degrees and 5 degrees.
Entry angle perception (retinal angle) from the bowler’s perspective vs. height.
In applying this assessment method, the difference between these two angles (3 degrees and 5 degrees) as viewed by the bowler is approximately 15 degrees. For example, if the height of the eye is 1.6 meters (5.3 feet), the angle of 3 degrees is perceived as 31 degrees and the angle of 5 degrees as 45 degrees. These angles are fairly easy to remember. Simply measure the height of the player’s eyes at the finish position and print the respective angles for memorization.
Finally, once the player has fully understood the entry angles of 3 degrees and 5 degrees, he can extrapolate from there to additional angles. For instance, knowing 3 degrees and 5 degrees, the player can easily see when the ball’s trajectory is between these memorized points and determine the angle to be 4 degrees. Equally an angle less than 3 degrees would be 2 degrees or slightly more than 5 degrees is 6 degrees. The ability of the player to determine the range of angles helps him assess the situation on the lane and ultimately provides the tools to consistently obtain the ideal entry angle during competition.